Question 41
After a small country begins permitting the import of automobiles, a foreign automobile manufacturer begins shipping cars to the country. This manufacturer can produce cars much more cheaply than the only manufacturer located in the country and therefore enjoys significant profits. What will erode the profits for the foreign manufacturer?
Question 42
A company reported income before taxes of $800,000 for Year 2. The company did not have temporary taxable differences at the end of Year 1 but reported a net deferred tax asset of $6,000 for Year 2. The effective income tax rate is 30 percent. What amount should the company pay as income tax for Year 2?
Question 43
A company is considering a project to develop a nascent technology to harness energy from ocean waves but wants to determine its economic viability. This 10-year project will cost the company $10 million in research and development costs and $25 million to build infrastructure. Each megawatt of energy costs $60 to produce, but the government offers a subsidy of $5 permegawatt. The price per megawatt of energy will be $56 for the next five years, and the company expects to produce 1 million megawatts per year. Ignoring the time value of money (i.e. assuming cash flows across different years are directly comparable), if costs, output, and subsidies remain constant, what will the market price of a megawatt of energy need to be in years six through ten to make this project economically viable?
Question 44
What can an analyst conclude about an industry that has a high level of government regulation, including permits and licenses?
Question 45
A company reported the following information for 2013: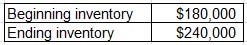
During 2013, the company purchased new inventory of $160,000. What amount should the company report as cost of goods sold on its 2013 income statement?

